CI/CD Pipelines Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide for Seamless Software Deployment

The Ultimate Guide to CI/CD Pipelines: Streamlined Software Delivery
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of software development, speed, reliability, and efficiency are paramount. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are the backbone of modern DevOps practices, enabling developers to deliver high-quality applications seamlessly and consistently.
This article will break down the steps involved in CI/CD pipelines, using the detailed flow diagram provided as a visual guide.
What is a CI/CD Pipeline?
A CI/CD pipeline is an automated framework that builds, tests, and deploys applications efficiently. It eliminates manual errors, standardizes processes, and ensures continuous delivery of reliable software updates. The pipeline handles everything—from code integration to live deployment—while maintaining the integrity of your application.
Understanding the CI/CD Workflow
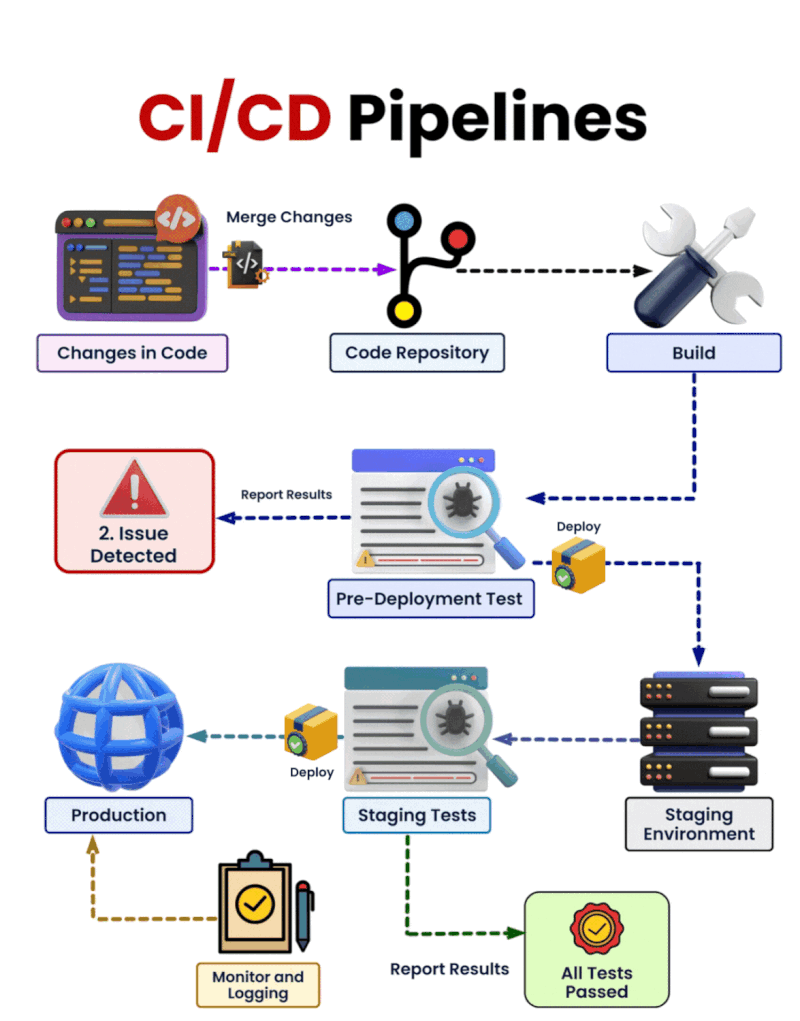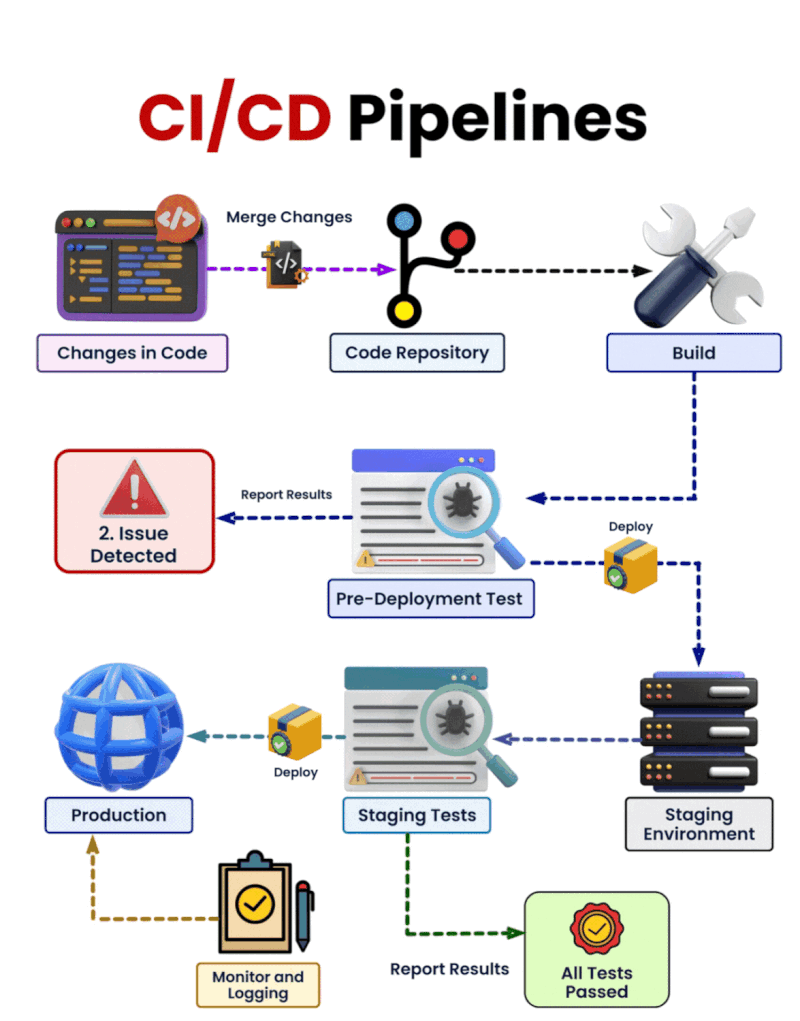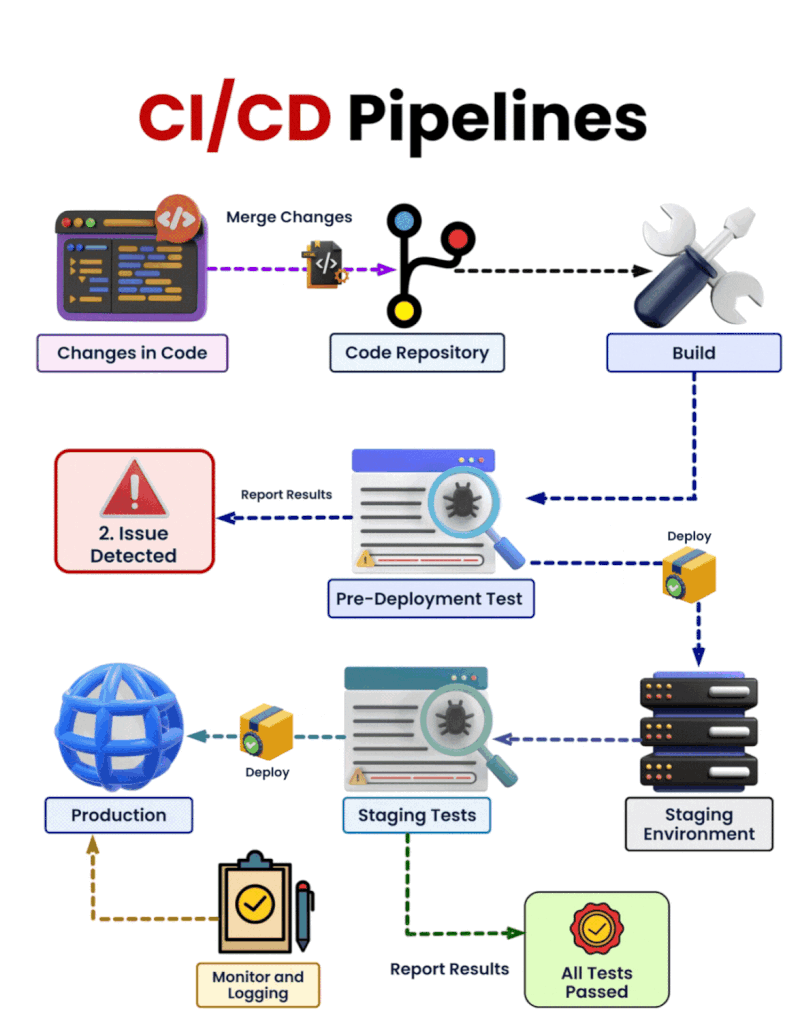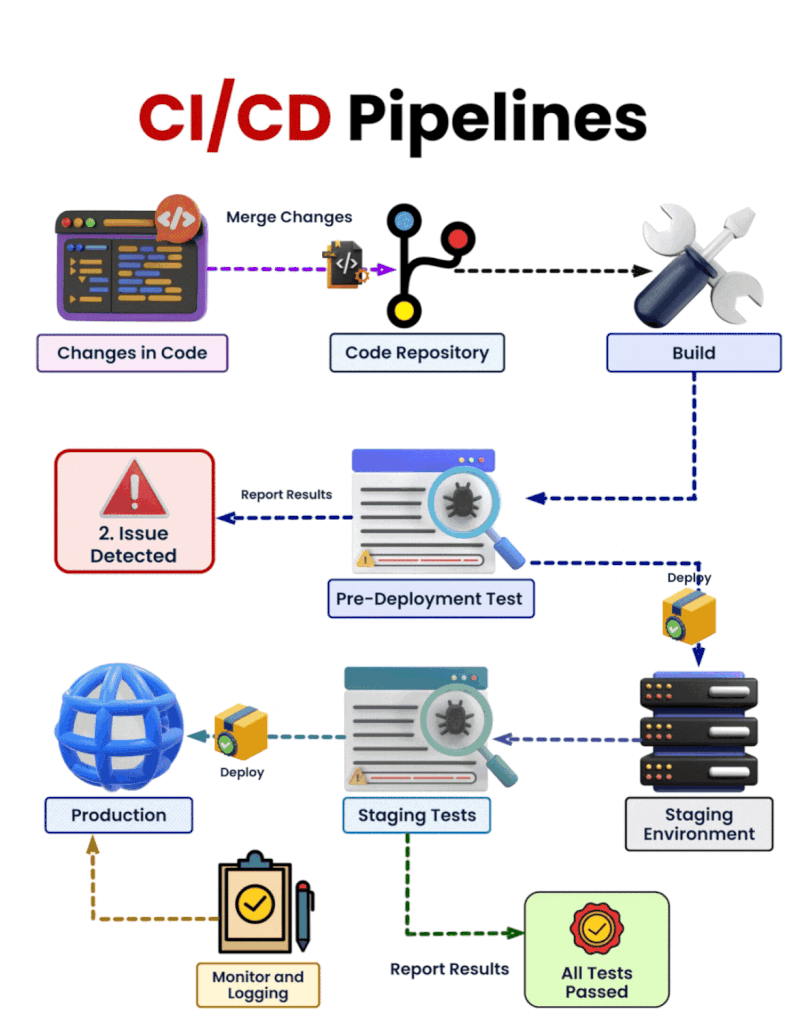
Let’s dive into the process, as depicted in the diagram:
-
Changes in Code
Developers write and modify code to add new features or fix bugs. Once ready, the changes are pushed to the code repository.- Key Insight: Proper version control and code management are essential to track and manage changes.
-
Code Repository
The repository acts as a centralized hub where all changes are stored and merged. Modern tools like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket are often used.- Purpose: Collaborate with team members and ensure a single source of truth for all code.
-
Build
After merging, the pipeline automatically compiles the code into a build. This step packages the application, preparing it for deployment.- Significance: Ensures the code is syntactically correct and ready for the next stages.
-
Pre-Deployment Test
Automated tests are triggered, including unit tests, integration tests, and occasionally end-to-end tests. These tests validate functionality and stability.- If an issue is detected, results are reported, and the pipeline halts for fixes.
-
Staging Environment
The successfully tested build is deployed to a staging environment, which mirrors production. Here, further testing like user acceptance testing (UAT) or performance testing occurs.- Goal: Verify the application in a near-production environment.
-
Staging Tests
Additional tests are run in staging to ensure the application is production-ready. Only if all tests pass does the pipeline proceed.- Outcome: Guarantees minimal risk of bugs or performance issues in production.
-
Production Deployment
The tested and approved application is deployed to the live environment, making it accessible to end users.- Deployment can either be automated or require manual approval, depending on the organization's requirements.
-
Monitor and Logging
Post-deployment, the application’s performance is monitored using tools like Prometheus, ELK Stack, or Datadog. Logs and metrics are analyzed to catch and resolve issues quickly.- Importance: Ensures a smooth user experience and quick response to incidents.
Benefits of CI/CD Pipelines
- Speed: Automates repetitive tasks, reducing deployment times.
- Quality Assurance: Identifies and resolves bugs early through automated testing.
- Consistency: Ensures uniformity across development, staging, and production environments.
- Scalability: Easily adapts to larger teams and projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the challenges in setting up a CI/CD pipeline?
1. Initial setup and configuration require expertise. 2. Integration with legacy systems can be complex. 3. Requires cultural alignment in teams for adopting DevOps practices.
Can CI/CD pipelines work for non-software projects?
Yes, CI/CD principles can be applied to infrastructure (e.g., Infrastructure as Code) and content deployment pipelines.
What tools are commonly used for CI/CD pipelines?
Popular tools include Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI, Travis CI, and Azure DevOps.